Lead with Clarity. Lead with Conviction. Lead with Intent.
Leadership often fails not because of strategy or talent, but because the message never lands with the force it needs. People follow direction only when they understand it, trust it, and feel the confidence behind it. That is the real work of assertive communication. It sits between silence and force. It allows you to say what needs to be said with clarity, with steadiness, and with respect.
Assertiveness is not volume. It is not dominance. It is the ability to speak with a clear mind, a steady tone, and a firm sense of what matters. When you communicate this way, people understand your expectations, your standards, and your priorities. They know you are present. They know you are intentional. They know you are accountable.
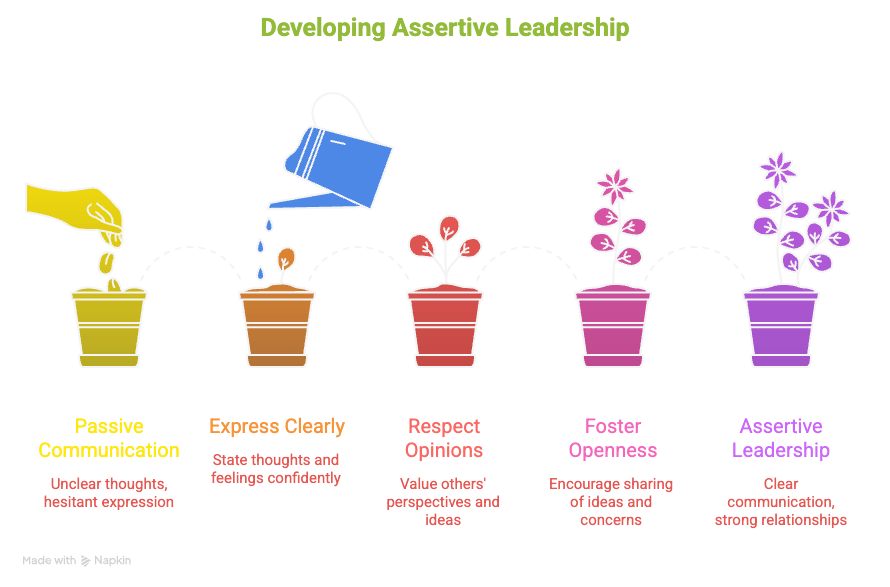
Assertiveness is not pushing harder. It is removing ambiguity. It is raising the standard.
The most effective leaders do three things consistently.
They speak with clarity instead of uncertainty.
They give direct feedback instead of indirect hints.
They set boundaries that protect focus instead of allowing everything to expand by default.
Clarity gives people direction.
Direct feedback gives them improvement.
Boundaries give them confidence in what matters.
You do not need aggressive language to lead with authority. You need structure in your thinking, simplicity in your message, and conviction in your delivery.
Assertiveness is learned. It is practiced. It is earned.
Great communicators prepare before the moment. They decide the outcome they want. They sharpen the point they need to make. They remove the noise that usually dilutes the message.
Three practices elevate this skill.
First, define your objective before you speak. If the goal is unclear, the message will drift.
Second, use clear first person language. This creates accountability and reduces defensiveness.
Third, evaluate yourself after every important exchange. The small corrections compound into mastery.
Assertiveness is not a personality trait. It is a discipline that strengthens with repetition. It reshapes your posture, your tone, your timing. It shifts how the room responds to you.
The payoff is not personal confidence. The payoff is organizational clarity.
When a leader speaks with conviction, three things happen.
People know what to do.
People know why it matters.
People know how their work connects to the mission.
This reduces conflict, accelerates decisions, and builds a culture where direction is consistent. Teams stop guessing. Meetings move faster. Feedback becomes normal. Accountability feels natural rather than punitive.
Assertive communication is not a stylistic choice. It is a leadership requirement. It turns complexity into direction. It turns hesitation into momentum. It turns effort into results.
Clarity builds trust.
Conviction builds credibility.
Intent builds alignment.
That is the work. That is the standard. That is the path forward.